Ensina LF, Min TK, Félix MMR, et al.
Front Allergy. 2022 Apr 15;3:840999. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.840999. eCollection 2022.
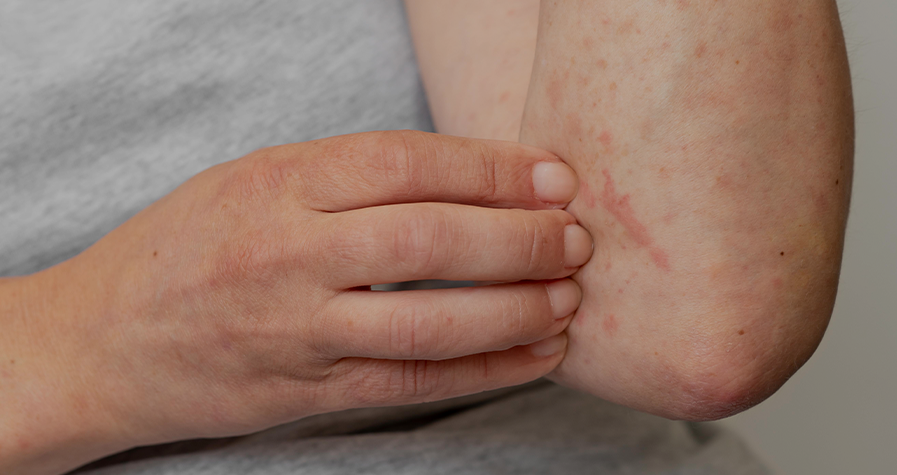
Acute urticaria is common and presents with wheals and/or angioedema. These symptoms are also frequent in anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction that must be immediately treated. In both conditions, mast cells have a central role in their mechanism of action. Although these similarities, the diagnostic approach is usually different, as it depends on the suspicious triggers, age of the patient and region where they’re based.
Anaphylaxis must be treated with adrenaline as first-line while urticaria flares can be treated with H1-antihistamines are the first choice.
The best approach to prevent anaphylaxis or acute urticaria episodes is to avoid the trigger that is responsible for the reaction, having in consideration that a solution may be desensitization to drugs and foods in selected patients to improve their quality of life.