In this study are investigated predictive biomarkers of disease evolution in a large cohort of children with seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (SAR).

Data on the clinical burden of chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) and economic consequences are lacking in France. To characterize the clinical and economic burden of CSU in symptomatic patients despite treatment by analysing data of French patients from the ASSURE-CSU study.

The findings of Alergológica 2015 show a notable increased frequency of allergic rhinitis, drug allergy, and food allergy. The frequency of other allergic conditions remained unchanged, except for asthma, whose frequency decreased, as in adult patients.
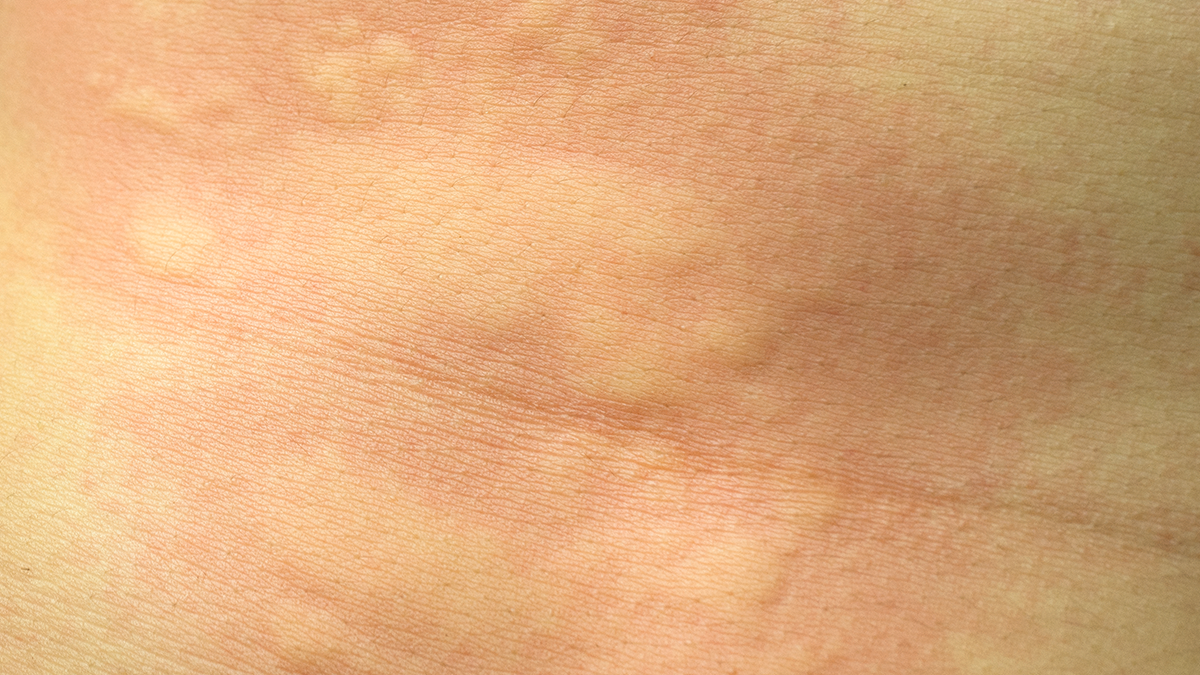
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is defined by the appearance of wheals and a variable presence of angioedema which persists for at least 6 weeks. Some groups are trying to detect molecules which would be able to help clinicians in reaching a proper diagnosis.

The aim of the present study was to investigate the levels of IL-22 and IL-17A in AR patients and their association with clinical severity of persistent allergic rhinitis (PAR).

Adherence to treatment is low in allergic rhinitis. This study shows an approach for measuring retrospective adherence based on a mobile app. This represent a novel approach also for analyzing medication taking behavior in a real-world setting.

Allergic rhinitis (AR) has been reported to be associated with chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of AR on nasal mucosa remodeling in CRS. AR could enhance the remodeling process in CRS. Moreover, Allergic rhinitis had different effects on chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and CRS without nasal polyps.
Chronic urticaria (CU) carries many risk factors for osteoporosis, but data on the relation between CU and osteoporosis are lacking. CU may impose a risk for osteoporosis. An appropriate targeted screening should be considered.sis en un gran estudio comunitario.
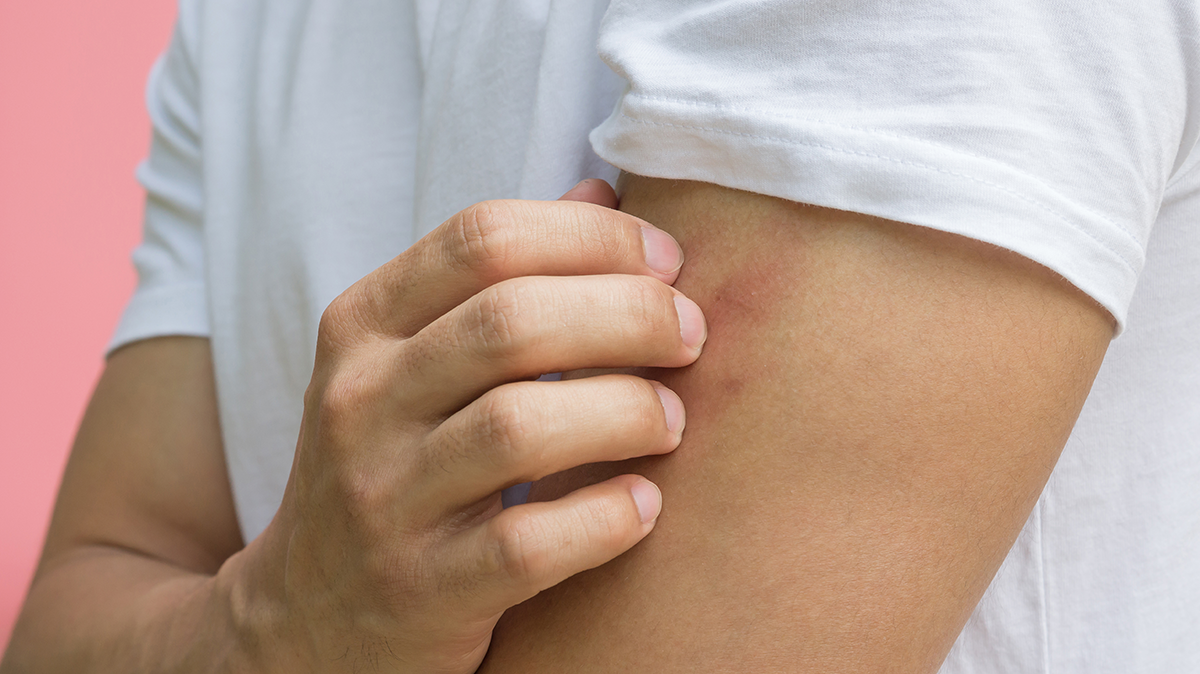
Chronic urticaria is an itchy skin disease, which is treated with antihistamines; however, a large group of patients are unresponsive to antihistamines alone and other treatments. This study presents an overview of studies investigating plasma D-dimer level as a biomarker for disease activity and treatment response in patients with chronic urticaria.

Chronic urticaria (CU) is a common disease, characterized by the development of wheals, angioedema, or both. CU reduces quality of life and can also cause emotional distress. The data of this study demonstrate that depression and anxiety symptoms are more common in patients with chronic urticaria than in the control group. Therefore, we should pay attention to the potential of mental comorbidities while managing patients with CU.

The prevalence of Allergic Rhinitis in OSA/SDB is considerably high and children with SDB suffering from a higher incidence of AR than non-SDB. OSA adults accompanied with AR do not have any influences on sleep parameters.
Allergic rhinitis (AR); obstructive sleep apnea (OSA); sleep-disordered breathing (SDB).




