Ana M. Giménez‑Arnau, Andaç Salman
Drugs . 2020 Aug 28. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01387-9. Online ahead of print.
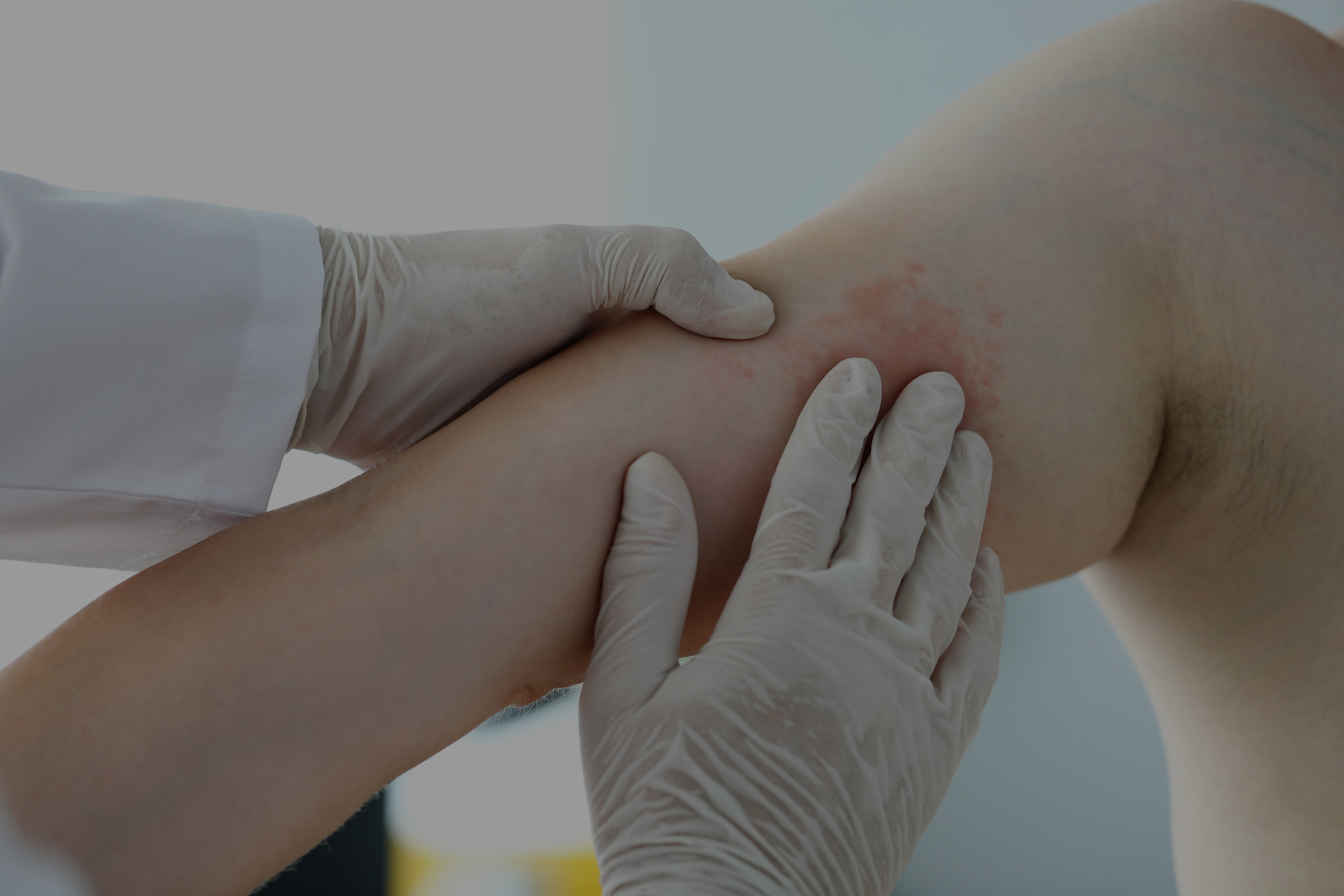
Chronic spontaneous urticaria is characterized by wheals, angioedema, or both for at least 6 weeks and can last for a long time, up to 5 years. The effects of chronic spontaneous urticaria on quality of life are comparable to psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, or even ischemic heart disease.
Antihistamines continue to be the first choice for treatment of urticaria, however rates of response are low (ranging from 38.6% in standard doses to 63.2% in higher doses), some patients don’t experience a complete of symptoms. The use of omalizumab has shown a major advance in treating patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria, however, there is a subgroup of patients who have a partial or even lack of response to omalizumab.
Some of the upcoming targeted therapies for chronic spontaneous urticaria include:
- anti-IgE antibodies, such as ligelizumab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the Cε3 domain of IgE and which has shown a six- to ninefold greater potency in vivo compared to omalizumab; UB-221, another monoclonal antibody against IgE with up to eightfold greater affinity for free IgE, compared to omalizumab; quilizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against membrane-bound IgE.
- Anti-Siglec-8. Siglecs are a transmembrane family with regulatory effects on intercellular and intracellular signaling, with Siglec-8 having expression on eosinophils and mast cells.
- Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) inhibitors. BTK is a tyrosine kinase expressed in hematopoietic cells, including macrophages, mast cells and basophils. BTK inhibitors are used to treat different malignancies of B-cell origin. Ibrutinib, dasatinib, AVL-292 and CNX-774 effectively suppressed IgE-induced activation and histamine release from basophils and mast cells.
- Chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expresses on Th2 (CRTH2) inhibitors; Spleen Tyrosine Kinase (SYK) inhibitors; Anti-CD20; Anti-IL-1; Anti-IL-4/13; and Anti-IL-5.
The future treatment of chronic urticaria will probably change once potential new treatments are completely developed.